Difference between revisions of "QOS Setup Guide"
Paul Falanga (talk | contribs) |
Drew Harrell (talk | contribs) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | QOS will enhance the function of Voice on the network in most cases. There are cases where the use of managed switches will likely not impact the performance of voice over the network but these are exceptions and IPitomy recommends using a Managed Switch on all commercially deployed implementations of voice products. | |
| − | QOS will enhance the function of Voice on the network in | + | |
| − | There are cases where the use of managed switches will likely not impact the performance of voice over the network but these exceptions and IPitomy recommends using a Managed Switch on all implementations of voice products. | + | First let me state that if already understand QoS and are just looking for where you set the DSCP value, Navigate to PBXSetup->SIP and under advanced go to SIP TOS and RTP TOS. Set these to any of the available class selector values, then set the selected class to be high priority in your switch. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.ipitomy.com/images/email_resource/qos_flash.swf Click here for brief illustration of how QOS works] (press the browser BACK button to return here) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If you have an unmanaged switch that supports QoS, you will need to consult the documentation but you can probably set CS5-7 and the switch should prioritize you over most traffic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | IPitomy performs QoS by tagging packets with DSCP values. DSCP refers to a field that is reserved for tags in every packet sent. This field has a value from 0-63. And manufacturers use many different names for the values in this field. One of the most prominent names for values are the "Class Selector" values. Their names start with "CS". But their decimal and binary values are below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center" | '''field name'''<br/> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center" | '''binary'''<br/> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center" | '''decimal'''<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF11<br/> | ||
| + | | 001010<br/> | ||
| + | | 10<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF12<br/> | ||
| + | | 001100<br/> | ||
| + | | 12<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF13<br/> | ||
| + | | 001110<br/> | ||
| + | | 14<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF21<br/> | ||
| + | | 010010<br/> | ||
| + | | 18<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF22<br/> | ||
| + | | 010100<br/> | ||
| + | | 20<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF23<br/> | ||
| + | | 010110<br/> | ||
| + | | 22<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF31<br/> | ||
| + | | 011010<br/> | ||
| + | | 26<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF32<br/> | ||
| + | | 011100<br/> | ||
| + | | 28<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF33<br/> | ||
| + | | 011110<br/> | ||
| + | | 30<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF41<br/> | ||
| + | | 100010<br/> | ||
| + | | 34<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF42<br/> | ||
| + | | 100100<br/> | ||
| + | | 36<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AF43<br/> | ||
| + | | 100110<br/> | ||
| + | | 38<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS1<br/> | ||
| + | | 001000<br/> | ||
| + | | 8<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS2<br/> | ||
| + | | 010000<br/> | ||
| + | | 16<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS3<br/> | ||
| + | | 011000<br/> | ||
| + | | 24<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS4<br/> | ||
| + | | 100000<br/> | ||
| + | | 32<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS5<br/> | ||
| + | | 101000<br/> | ||
| + | | 40<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS6<br/> | ||
| + | | 110000<br/> | ||
| + | | 48<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CS7<br/> | ||
| + | | 111000<br/> | ||
| + | | 56<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EF<br/> | ||
| + | | 101110<br/> | ||
| + | | 46<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | default<br/> | ||
| + | | 0<br/> | ||
| + | | 0<br/> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The important thing with configuring QoS is understanding how a switch "sees" your packets and how a priority is used in your particular equipment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the first part: Does the switch trust the values you set on packets or does it just wipe them out and put another value? This is often defened as a DSCP "Trust" Mode. Does the switch trust what it sees or does it set the value everything on port x to a hard-coded value? | ||
| + | |||
| + | Many switches implement 4 queues, with the higher number queue being the highest prescedence. These queues are then mapped into 7 classes or categories of traffic. Normally by default the classes are also configured such that the higher number is using the highest queue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The implementation of QOS varies greatly from one switch manufacturer to another and therefore we have decided to post this guide for one of the switches for which we have experience, the Netgear FS728TP. '''(Note: many switch manufacturers set CS3 {IPitomy Default} to Low or Normal Priority. When the switch manufacturer states "QOS is ON at default" do not assume you can just plug it in and it'll do what you hope it will do.)''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Netgear FS728TP product specs are available at: [http://www.netgear.com/business/products/switches/smart-switches/FS728TP.aspx http://www.netgear.com/business/products/switches/smart-switches/FS728TP.aspx] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This is a concise description of how QOS is implemented(by Netgear): [http://www.ipitomy.com/images/email_resource/QoS_on_Netgear_Switches.pdf http://][http://www.ipitomy.com/images/email_resource/QoS_on_Netgear_Switches.pdf www.ipitomy.com/images/email_resource/QoS_on_Netgear_Switches.pdf] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
We like the switch because it is cost-effective and efficiently performs the tasks required to optimize a network for voice traffic. | We like the switch because it is cost-effective and efficiently performs the tasks required to optimize a network for voice traffic. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 129: | ||
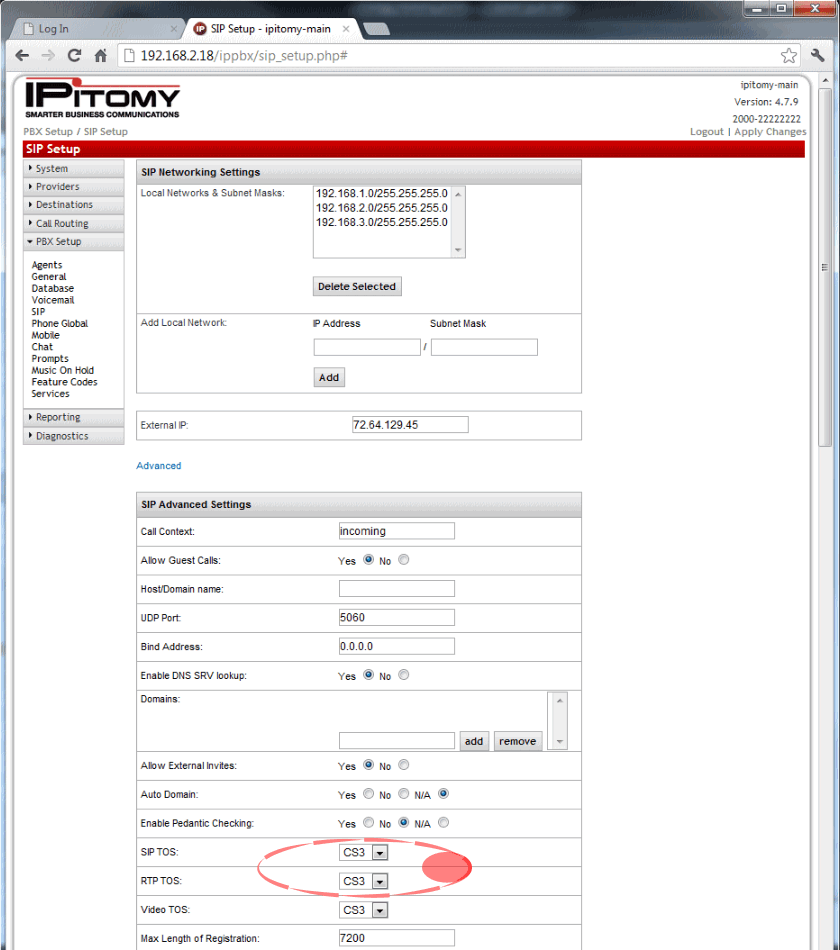
For reference only the QOS setting in the PBX is shown: | For reference only the QOS setting in the PBX is shown: | ||
| + | <blockquote>[[File:PBX GUI - SIP Advanced.gif]]</blockquote> | ||
| + | Notice the SIP TOS and RTP TOS are set to "CS3"... this is a reference to make QOS programming easier. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The type of service (TOS) field in the IPv4 header has had various purposes over the years, and has been defined in different ways by five RFCs[1]. The modern redefinition of the TOS field is a six-bit Differentiated Services Field (DS field)[2] field and a two-bit Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) field.[3] While Differentiated Services is somewhat backwards compatible with TOS, ECN is not. (Source: Wikipedia [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_of_Service http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_of_Service]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other VERY helpful information: | ||
| − | [ | + | [http://bytesolutions.com/Support/Knowledgebase/KB_Viewer/ArticleId/34/DSCP-TOS-CoS-Presidence-conversion-chart.aspx DSCP-TOS-CoS-Presence conversion chart] |
| − | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differentiated_Services_Code_Point DiffServ Refrence] | |
| − | + | ;Step 1. | |
| + | :Navigate to the switch (we recommend setting the switch or switches to Static IP Address assignments since these are infrastructure devices that must be maintained and often require remote access. (The setting of Static IP Addressing for the switch is not covered in this guide but is very easily done under the heading of System - Management - IP Configuration.)<br/>[[File:Netgear Loging Screen.gif]] | ||
| − | Step | + | ;Step 2. |
| + | :Input the password ("password' at default) | ||
| − | + | ;Step 3. | |
| + | :Navigate to the QOS tab | ||
| − | Step | + | ;Step 4. |
| + | :Navigate to Basic - CoS Global Configuration | ||
| − | Step | + | ;Step 5. |
| + | :Enable QoS | ||
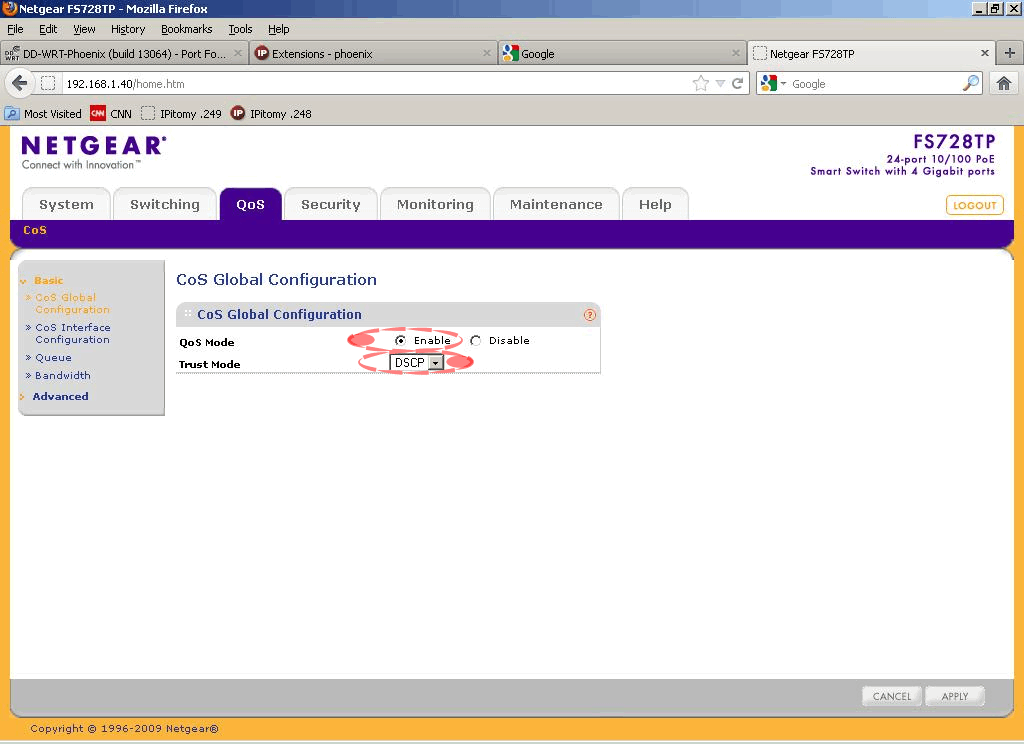
| − | Step | + | ;Step 6. |
| + | :Set the trust mode to DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point)<br/>[[File:Netgear QOS Screen.gif]] | ||
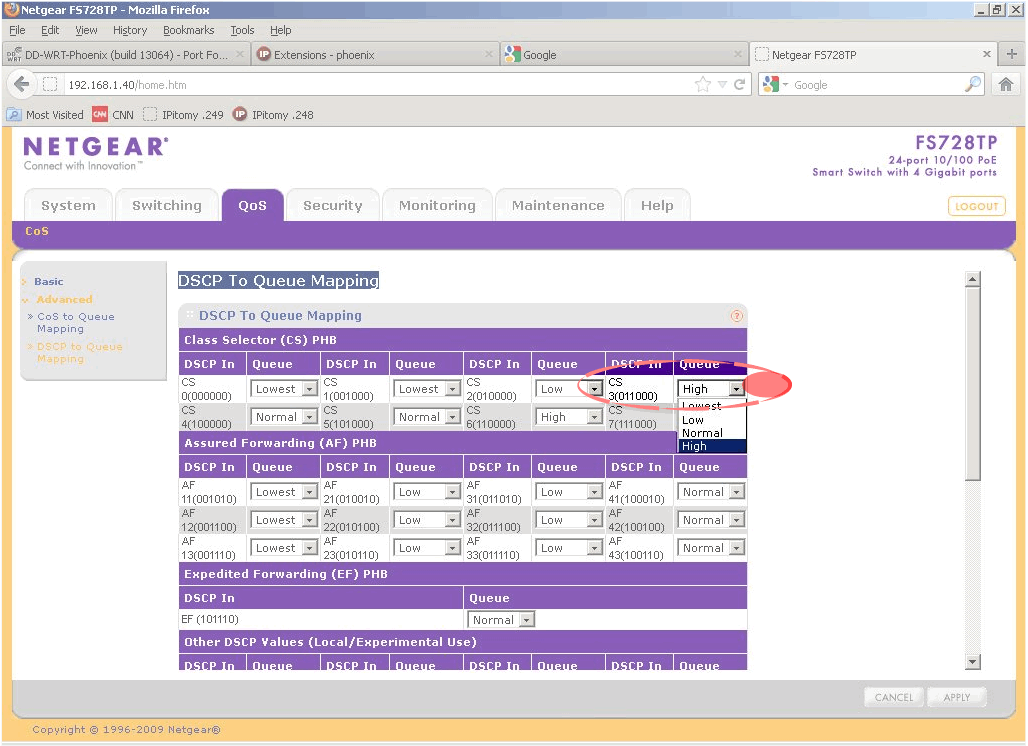
| − | Step | + | ;Step 7. |
| + | :Navigate to Advanced - DSCP to Queue Mapping<br/>[[File:Netgear DSCP to Queue Mapping.gif]] | ||
| − | Step | + | ;Step 8. |
| + | :Under Class Selector (CS) PHB select the queue priority High from the list for CS3 | ||
| − | + | ;Step 9. | |
| + | :Select Apply | ||
| − | + | That's it! QOS is now set on this switch to prioritize voice traffic over non-voice traffic. | |
| − | [[ | + | [[Category: Troubleshooting|QoS Setup]] |
Latest revision as of 22:24, 25 April 2013
QOS will enhance the function of Voice on the network in most cases. There are cases where the use of managed switches will likely not impact the performance of voice over the network but these are exceptions and IPitomy recommends using a Managed Switch on all commercially deployed implementations of voice products.
First let me state that if already understand QoS and are just looking for where you set the DSCP value, Navigate to PBXSetup->SIP and under advanced go to SIP TOS and RTP TOS. Set these to any of the available class selector values, then set the selected class to be high priority in your switch.
Click here for brief illustration of how QOS works (press the browser BACK button to return here)
If you have an unmanaged switch that supports QoS, you will need to consult the documentation but you can probably set CS5-7 and the switch should prioritize you over most traffic.
IPitomy performs QoS by tagging packets with DSCP values. DSCP refers to a field that is reserved for tags in every packet sent. This field has a value from 0-63. And manufacturers use many different names for the values in this field. One of the most prominent names for values are the "Class Selector" values. Their names start with "CS". But their decimal and binary values are below:
| field name |
binary |
decimal |
| AF11 |
001010 |
10 |
| AF12 |
001100 |
12 |
| AF13 |
001110 |
14 |
| AF21 |
010010 |
18 |
| AF22 |
010100 |
20 |
| AF23 |
010110 |
22 |
| AF31 |
011010 |
26 |
| AF32 |
011100 |
28 |
| AF33 |
011110 |
30 |
| AF41 |
100010 |
34 |
| AF42 |
100100 |
36 |
| AF43 |
100110 |
38 |
| CS1 |
001000 |
8 |
| CS2 |
010000 |
16 |
| CS3 |
011000 |
24 |
| CS4 |
100000 |
32 |
| CS5 |
101000 |
40 |
| CS6 |
110000 |
48 |
| CS7 |
111000 |
56 |
| EF |
101110 |
46 |
| default |
0 |
0 |
The important thing with configuring QoS is understanding how a switch "sees" your packets and how a priority is used in your particular equipment.
For the first part: Does the switch trust the values you set on packets or does it just wipe them out and put another value? This is often defened as a DSCP "Trust" Mode. Does the switch trust what it sees or does it set the value everything on port x to a hard-coded value?
Many switches implement 4 queues, with the higher number queue being the highest prescedence. These queues are then mapped into 7 classes or categories of traffic. Normally by default the classes are also configured such that the higher number is using the highest queue.
The implementation of QOS varies greatly from one switch manufacturer to another and therefore we have decided to post this guide for one of the switches for which we have experience, the Netgear FS728TP. (Note: many switch manufacturers set CS3 {IPitomy Default} to Low or Normal Priority. When the switch manufacturer states "QOS is ON at default" do not assume you can just plug it in and it'll do what you hope it will do.)
The Netgear FS728TP product specs are available at: http://www.netgear.com/business/products/switches/smart-switches/FS728TP.aspx
This is a concise description of how QOS is implemented(by Netgear): http://www.ipitomy.com/images/email_resource/QoS_on_Netgear_Switches.pdf
We like the switch because it is cost-effective and efficiently performs the tasks required to optimize a network for voice traffic.
For best performance, ports on a switch should be designated for either non-voice data (PC's, printers, etc.) or voice-data. This isn't always possible but since QOS can be set as part of the packet header, its efficiency can still be realized.
In the FS728TP QOS is set as follows:
For reference only the QOS setting in the PBX is shown:
Notice the SIP TOS and RTP TOS are set to "CS3"... this is a reference to make QOS programming easier.
The type of service (TOS) field in the IPv4 header has had various purposes over the years, and has been defined in different ways by five RFCs[1]. The modern redefinition of the TOS field is a six-bit Differentiated Services Field (DS field)[2] field and a two-bit Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) field.[3] While Differentiated Services is somewhat backwards compatible with TOS, ECN is not. (Source: Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_of_Service)
Other VERY helpful information:
DSCP-TOS-CoS-Presence conversion chart
- Step 1.
- Navigate to the switch (we recommend setting the switch or switches to Static IP Address assignments since these are infrastructure devices that must be maintained and often require remote access. (The setting of Static IP Addressing for the switch is not covered in this guide but is very easily done under the heading of System - Management - IP Configuration.)
- Step 2.
- Input the password ("password' at default)
- Step 3.
- Navigate to the QOS tab
- Step 4.
- Navigate to Basic - CoS Global Configuration
- Step 5.
- Enable QoS
- Step 8.
- Under Class Selector (CS) PHB select the queue priority High from the list for CS3
- Step 9.
- Select Apply
That's it! QOS is now set on this switch to prioritize voice traffic over non-voice traffic.