Training:Application Solution
IPitomy Technical Training – Basic: Understanding the Application
Overview
At IPitomy, we believe in crafting a PBX solution that precisely meets our customer's requirements. The key to achieving this is thorough information gathering from the customer. This information forms the basis of your IPitomy setup worksheet, a critical document defining the scope of work for system programming. Having this documented ensures alignment of expectations and serves as a reference for system reconstruction, if necessary.
Database Building:
Database Building in IPitomy's IP PBX System
At IPitomy, our IP PBX system represents the cutting edge of business telecommunications, functioning as a software-centric solution. This approach distinguishes it from traditional Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) based key systems and PBXs. The primary advantage of our software-based system is its minimal reliance on hardware components, significantly reducing the likelihood of hardware failures.
Effective database construction within our system is crucial and should be meticulously planned. This planning process is vital to ensure that the final solution aligns perfectly with customer expectations. Gathering detailed information prior to the installation date is essential for a smooth, professional installation process and to minimize unbillable follow-up work.
One of the standout features of the IPitomy system is its user-friendly, web-based administration interface. This interface simplifies the programming and setup of the application. It's important to note that the IPitomy system does not include a default database. Therefore, setting up the database requires careful attention to sequence to establish the necessary elements for successful call flow.
Key Components of Database Building
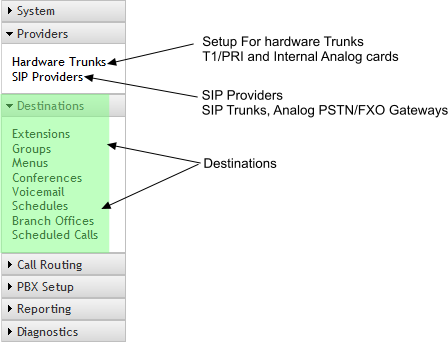
- Destinations:
- In the IPitomy system, destinations are the endpoints within the PBX where calls are routed. Examples include automated attendants or individual extensions.
- Direct Inward Dialing (DID) numbers can be assigned to directly route calls to specific destinations, such as conference rooms or individual extensions, enhancing direct communication efficiency.
- Providers (Trunks):
- Providers in the IPitomy system are crucial elements that manage the routing of calls both into and out of the system.
- Once destinations are established, providers can be set up to facilitate the designed call routing requirements. This setup is integral to ensuring that calls are managed and directed according to specific business needs.
By following these steps and understanding the intricacies of our IPitomy IP PBX system, users can leverage its full potential to create a robust, efficient telecommunication setup that meets and exceeds customer expectations.
The Application Development Sequence:
Creating Extensions:
- Extension Configuration:
- Extensions are configurable as 3 or 4-digit numbers.
- Features include various Call Forwarding options such as Unconditional, Busy, No Answer, or Unavailable.
- With the creation of an extension, a corresponding voicemail box, a chat client, and a schedule are automatically generated.
- The 'Follow-Me' feature enhances flexibility by allowing simultaneous and sequential ringing across multiple extensions or PSTN numbers.
- Licensing and Extension Management:
- The total number of available extensions is governed by the licensing agreement, with options for expansion to cater to growing business needs.
- Separate licensing categories exist for IPitomy phones and non-IPitomy devices, with open extension licenses typically carrying a slightly higher cost.
- The system provides Auto Provisioning for IPitomy Phones, streamlining the setup process.
- Importing user information through a CSV file is a time-efficient method to batch-create extensions.
- Manual creation of extensions is also an option, allowing for individualized data entry.
- Mass editing features are available post-creation, facilitating easy management and updates of extension information.
- System Compatibility and Intercom Use:
- The IPitomy system boasts wide compatibility with a range of SIP devices, including conference phones, softphones, and other SIP-compliant equipment.
- An added feature is the capability of using IPitomy phones for intercom paging, either between individual extensions or groups, enhancing internal communication efficiency.
Creating Groups of Extensions:
- Group Functionality and Customization:
- Groups can be configured to ring all extensions at once or in a specific sequence, depending on the organizational needs.
- Advanced group functionalities offer remarkably flexible call coverage, accommodating diverse communication strategies.
- Priority settings within groups enable automatic call assignment to specific members during peak times, bypassing the need for manual login.
- Timeout settings can be programmed to redirect calls to alternative destinations after a set duration.
- The agent ring time feature allows for the re-initiation of the ring sequence to include members who have just concluded other calls.
- Groups typically function as hubs for routing incoming calls to a department or team.
- Groups can also be utilized for paging purposes, with both unicast call paging and multicast paging options.
- The system allows for customization of caller ID information, and unique Music on Hold or Message on Hold can be assigned to each ring group.
Creating Menus and Recording Prompts:
- Automated Attendant Configuration::
- Menus in the IPitomy system serve as single-digit dialing destinations, simplifying the call routing process for callers
- Users can record prompts using the in-built prompt recording utility, ensuring clarity and professionalism in automated responses.
- Planning and pre-recording prompts are advisable for efficient onsite configuration.
- The system also supports the uploading of pre-recorded prompts, providing flexibility in the creation and management of automated attendants.
Additional System Features & Destinations
- Conference Bridge Implementation:
- The system includes default conference bridge destinations (901 and 902), each accommodating up to 32 participants.
- Additional conference bridge destinations can be activated through license expansion, catering to larger or multiple simultaneous conferences.
- Customizable greetings can be set for conference rooms, providing a personalized experience for participants.
- Integrated Voice Mail System:
- Voice mail boxes are automatically created for each extension, streamlining the setup process.
- The integrated nature of the voice mail system eliminates the need for manual forwarding, with default settings to forward calls to voice mail after 32 seconds of inactivity.
- Scheduling and Time-Based Routing:
- The scheduling feature in the IPitomy system allows for the dynamic routing of calls based on the time of day, enhancing flexibility in call management.
- Schedules can be customized to route calls differently during business hours, after hours, and during specific intervals like lunch breaks.
- This feature can be implemented at various points in the call path to facilitate time-sensitive call routing.
- Branch Office Connectivity:
- The branch office destination feature enables seamless call routing to other IPitomy IP PBX Systems.
- Extensions within branch offices are easily accessible, maintaining organizational coherence across multiple locations.
- A unique dialing code is available to connect extensions that share the same number in different branches.
- Scheduled Call Announcements:
- This feature allows for the automated playing of announcements or audio files to a group of phones or integrated paging devices based on a preset schedule.
- Practical applications include school bell sounds to mark the start and end of classes or emergency announcements triggered by dialing a specific extension and entering a PIN code.
Review and Confirmation Process in IPitomy System Setup
The final stage in setting up an IPitomy IP PBX system is a comprehensive review and confirmation process. This ensures complete alignment of the system components with the customer's specifications and requirements. Documenting all relevant information in the IPitomy Setup Worksheet is crucial for defining the scope of work and establishing clear expectations between the provider and the customer.
Extension Number Range
- Confirm the range of extension numbers to be used, ensuring they fit the customer's organizational structure and communication needs.
Device Types
- Document the types of devices integrated into the system, including IP phones, conference devices, and other SIP-compatible hardware.
Network Layout
- Examine and confirm the overall network layout, assessing its compatibility and efficiency for the IPitomy system.
Router Specifications
- Ensure understanding of the router's capabilities, crucial for network settings configuration and system integration.
Data Switch Types
- Identify data switch types, particularly noting Power over Ethernet (PoE) capabilities, essential for planning device connectivity and power management.
Cabling
- Check that network cabling is certified and in good condition, and that all devices and IP addresses are accurately documented.
Router Access
- Secure access to the router GUI or establish a relationship with IT personnel for necessary access.
IP PBX IP Address
- Confirm the uniqueness of the IPitomy system's IP address within the network to avoid conflicts.
Network Condition
- Assess the overall health and performance of the network, ensuring it can adequately support the IPitomy system.
End-User Network Responsibility
- Ensure that the end-user understands their role in maintaining network performance, including the necessity of network upgrades or modifications for optimal system functioning.
Application Development
Voice Mail Email
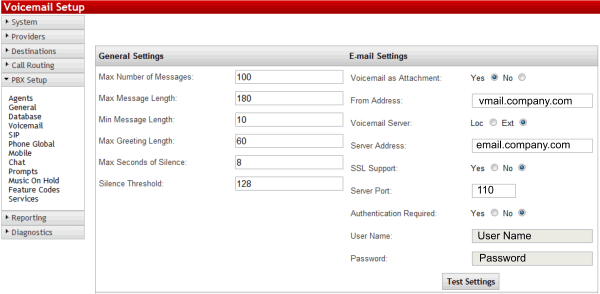
In order for the IP PBX System to send out emails, it is necessary to have an email account assigned to the system so all emails that the system sends out can be from a legitimate email account. This is entered into the system under <PBX Setup> <Voicemail>. See the screen below.
Once the email settings are properly configured for sending emails, all that is required is to add the users email address in the extension. Omitting the email address turns off the email feature in each extension. if you are not using Voice mail to Email, do not put an email address in the email address field on the extension screen.
Email needs to be setup for sending out of the PBX to the customer's email system.
- Sent From
- The customer must provide an Email account for the Voice Mail system (vmail@company.com) on their Email Server and use that email account so all emails from the IP PBX System will be sent using the accounts email credentials.
- If no email server is available to create an account, creating one on Google GMail (vmail.company@gmail.com) or another similar service. Be sure to prepare for this in advance and have an email account and password ready when you go to do the installation. If you neglect to do this, it will add to your installation time.
Ring Groups/ACD
- Ring Groups Defined – Ring Groups are a powerful communications resource in the IPitomy IP PBX and for your customer.ACD will be discussed in the Advanced training course.
- Ring Strategy
- Go to the IPitomy WIKI at http://wiki.ipitomy.com
- Select the IPitomy PBX Plus Administration Guide
- Select Groups or search for - Ring Stategy - The WIKI will have all of the information required to set up ring groups.
- Members – those in the group with physical telephones. Members are permanent devices in the Queue. Members have the ability to place their device into Pause thereby removing themselves from queued calls, however this also eliminates all incoming calls except Page Announce Call
- Agents – those in the group with no specific telephone or wanting the ability to Log On to the Queue and Log Off the Queue separately from telephone-based functions. Agents can log in from any phone. - Requires ACD Option
- Failovers (Queue Timeout destinations) Where the call is directed to after the timeout expires. This can be any destiniation in the system.
- Will a menu be associated to any Ring Groups (ACD Feature – callers in an ACD - Ring Group queue can interact with options available while waiting in queue and select a new system destination)
- Use theIPitomy WIKI at http://wiki.ipitomy.com to search for any of the subjects above to learn about how to implement the powerful features of Ring Groups and ACD.
- Link to Group Video Training [1]
Menus
- Menus defined
- Auto Attendant, and subsequent menus must be planned in advance and well organized to allow for a streamlined installation of that portion of the application.
- Get prompts scripts – write them or have them prepared for you by the user
- Get Destination selections for one-digit dialing
- Determine if extension dialing will be allowed and at what menus
- Determine Menu overflow Destinations – where callers will be routed when they dial:
- nothing
- incorrectly
- Link to Video Training [2]
Schedules
- Determine schedules
- Day Hours of operation
- Lunch Hour
- Night Hours of operation
- The “Attendant” assigned telephone may be given the ability to select the Day/Night mode of operation
Branch Office
- If a Branch Office is to be part of this application the numbering plan and menus must be known for that system and it must be deployed with equal attention to detail.
Determine:
- If extension numbering at the branch office is to be transparent to the users (users may dial any extension number regardless of branch location or local PBX location with no special coding or prefix erquired). If so, the extension number scheme at the branch office must not conflict with extension numbering at this PBX or any other branch office.
- Shared Name for the Branch – this name will be applied to both PBX locations to allow them to meet (connect) over the interlinking network (Internet usually)
- Code for branch access – this code can be mirrored at each branch and used to access the paired branch
- Branch Password – this password will be applied to both PBX locations to allow them to meet (connect) over the interlinking network (Internet usually)
Remote Phone(s)
- If remote phones are to be used, assure that the router has been programmed to allow BOTH UDP and TCP Packet forwarding (Port 5060 should be configured for UDP and Ports 10,000-20,000 should be configured for UDP)
- Assure that the bandwidth at the remote phone location is adequate to handle call traffic for each telephone – especially when multiple phones are deployed at remote locations. (Plan for 200kb/s for each, two-way voice call.)
- If more than five remote phones are to be used at any remote site concurrently, consider installing an IP PBX at that location as a Branch Office instead.
- QOS is essential to all lans with VoIP traffic. We recommend setting QOS if possible to make voice call traffic a higher priority than other data traffic.
- Disable ALG (Application Layer Gateway). This router function can be powerful but a nuisance to voice traffic.
- If a Sonicwall is in use, review notes in IPitomy’s Sonicwall Configuration guide at:
http://www.ipitomy.com/webrelease/Sonicwall/Sonicwall%20Quick%20Guide.pdf - Go to PBX Setup=>Phone Global
- enable Phone Download Enabled
- enable Phone Auth Enabled
- note the user and pass to be manually entered later (since the phone is already remote)
- Click Save and Apply Changes
Edit the Phone settings for the extension (pencil with handset)
- Change the Configuration Updates protocol to HTTP
- Click Save & Configure Phone button (were the phone local, the correct values would be sent to the phone)
Manually Changing in phone
- Log into phone via IP Address (user: root, pass: root)
- Navigate to Phone Maintenance=>Autoprovision
- Change Protocol to HTTP
- Enter Username and Password from earlier Phone Global steps
- Change the Software Server URL to: http:///ippbx/phonecfg/ - - Click Submit and wait for the phone to become idle
- Refer to this section of the manual : Remote_Phones
Below is how you include the remote phones section:
QManager
- Desktop Call Manager is a PC-based, Windows Application that can be loaded onto user computers to gain a high level of control of communications for their telephone. DCM is licensed per user and can be installed at on a single PBX or multiple PBX’s that are branched together with the Multisite DCM License.
- Since Desktop Call Manager integrates a Chat Client, DCM links the desktop to the world of chat and SMS Texting.
- Presence – DCM enables a presence indication via its integrated Chat client.
- DCM Provides the user with:
- Ability to monitor selected extensions on the IP PBX and Branch Office IP PBX’s
- Monitor call traffic at the monitored extensions
- Interact with call traffic at the monitored extensions
- Listen
- Whisper
- Barge
- Record calls in progress at that extension (Recordings via DCM are stored in the DCM application)
- Interact with callers in voicemail
- Screen caller leaving messages in voice mail
- Pick up (retrieve) callers from voice mail
- Record calls in progress at their own extension (Recordings via DCM are stored in the DCM application)
- Monitor Park Locations
- Monitor Trunks
- Utilize DCM-based Speed Dial
- Send and Receive Text Messages (a Chat server is required – any may be used)
- Monitor Conference Rooms 901 902… and other if licensed/programmed
- DCM may be used to invoke PBX functions:
- Dial
- Transfer
- Park
- Hang up
- Call and Extension
- Page an Extension
- Call Forward – DCM can be used to monitor PC activity and invoke pre-programmed call forward scenarios when a PC user is inactive for 15 minutes
- Interact with callers in voicemail
Multisite Desktop Call Manager
- Both sites must be Multi Site Licensed and Multi Site Enabled
- MUST be enabled in the Branch office settings
- You MUST Port Forwards Ports 5048 and 5038 to the IP of the PBX at each router
- You must set up the ACL in the IP PBX to allow the mated branch office to connect on Ports 5038 and 5048. (The default only allows for local IPs).
Questions:
- T/F, A Branch Office extension can be dialed directly without a branch office code regardless of which extension and branch where the extension is installed.
- What benefit comes from setting up a Sent From email address.
a. puts the Sent From email address in front of the user each time an email from the IP PBX is received.
b. puts the Sent From email address in front of the user each time an email is received.
c. The email address set as Sent From becomes the server for all emails that are IP PBX generated
d. The Sent From email address defines which email that are received are valid. - T/F, When DCM is used at a branch office a Multisite license must be purchased at only the IP PBX that is the Branch Office IP PBX.
- T/F, A Menu can be assigned to a ACD Group so that callers may dial a single digit and while waiting in queue and be directed to another system destination.
Where on the WWW can you go to find the IPitomy Installation and Maintenance Manual?
http://wiki.ipitomy.com
or
http://www.ipitomy.com/webrelease/IPitomy/IP1100+/IPitomy%20IP1100+%20Manual.pdf