Training:Install Preparation
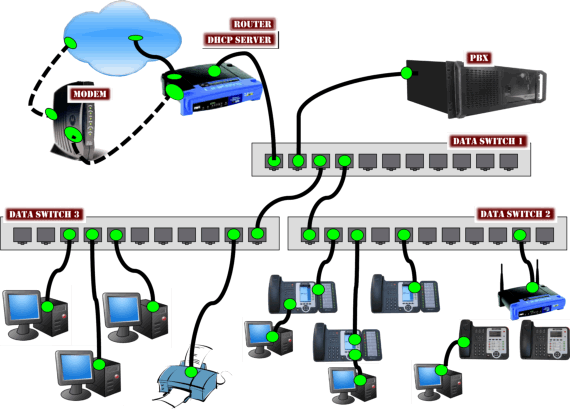
Before proceeding with the installation, it is crucial to identify the data switch that will be used, or recognize the existing switches at the site. We recommend utilizing a Level 2 managed switch, as it supports Quality of Service (QoS). Implementing QoS assures high-priority handling of voice traffic, thus improving call quality and overall performance. The switch you deploy is a fundamental component of your network's backbone.
When mapping out your network, consider the configuration and layout critically. Technicians often commit errors in network design, inadvertently creating unnecessary bottlenecks. For instance, if you have 20 phones connected to a 24-port switch, it would be optimal to connect the IPitomy PBX to this same switch. This setup ensures all voice network packets remain within the same hardware, optimizing network efficiency.
Another key consideration is the Power over Ethernet (PoE) option. PoE technology allows for the transmission of electrical power, along with data, over Ethernet cabling in a safe manner. The IEEE standard for PoE mandates Category 5 cable or above for high power levels, but Category 3 cable can suffice for lower power levels. Power is delivered in common mode over two or more of the differential pairs of wires found in Ethernet cables, sourced either from a power supply within a PoE-enabled networking device like an Ethernet switch or injected into a cable run with a midspan power supply.
The initial IEEE 802.3af-2003 PoE standard can provide up to 15.4 W of DC power (minimum 44 V DC and 350 mA) to each device, with 12.95 W guaranteed to be available at the powered device as some power loss occurs in the cable.
The subsequent IEEE 802.3at-2009 PoE standard, also referred to as PoE+ or PoE plus, can supply up to 25.5 W of power. This standard prevents a powered device from using all four pairs for power. However, some vendors have developed products claiming compatibility with the 802.3at standard, offering up to 51 W of power over a single cable by leveraging all four pairs in the Category 5 cable.
IPitomy telephones typically consume 7 watts of power or less, making them highly compatible with these PoE standards.
Before the standardization of PoE, various non-standard schemes were employed to deliver power over Ethernet cabling. Some of these schemes are still in use today, although adherence to IEEE standards is typically recommended for compatibility and safety reasons.
|
Speed [Mbit/s] |
Distance [m] |
Name |
Standard |
Description |
|
1 |
100 (nominally) |
802.3e 1986[9] |
Runs over four wires (two twisted pairs) on telephone twisted pair or Category 3 cable. An active hub sits in the middle and has a port for each node. Manchester coded signaling. | |
|
10 |
100 (nominally) |
(pre) 802.3i 1987 |
Runs over AT&T Premises Distribution System (PDS) wiring or four wires (two twisted pairs) on telephone twisted pair or Category 3 cable.[3][10] | |
|
10 |
100 (nominally)[11] |
10BASE-T |
802.3i 1990 |
Runs over four wires (two twisted pairs) on a Category 3 or Category 5 cable. Star topology with an active hub or switch sits in the middle and has a port for each node. This is also the configuration used for 100BASE-T and gigabit Ethernet. Manchester coded signaling. |
|
100 |
100 |
802.3u 1995 |
4B5B MLT-3 coded signaling, CAT5 copper cabling with two twisted pairs. | |
|
1000 |
100 |
802.3ab 1999 |
PAM-5 coded signaling, At least Category 5 cable, with Category 5e strongly recommended copper cabling with four twisted pairs. Each pair is used in both directions simultaneously. | |
|
10 000 |
100 |
802.3an 2006 |
Uses category 6a cable. |
Installation:
When installing the system it is best to use the following outline:
- Create Extensions
- Import – extensions are created by importing a CSV file
- Auto Discovery - PBX used to discover all phones on the network
- Auto Provision – PBX pairing function to install extensions
- Data Entry - one at a time
- Create Groups
- No limit to Groups
- Use for Department calling patterns
- Ring Strategies to be used
- Queue handling
- Create Menus
- Unlimited Menus
- Use for instructions/announcements
- Use for call routing
- Create Trunks
- SIP – Provider and SIP Configuration known and in-hand
- Hardware
- T-1, PRI
- DID destination
- Default Answering Destination
- Internal Gateway (PBX board for PSTN)
- Default Answering Destination
- T-1, PRI
- Inbound Routing
- Outbound Routing
Test as you go
- configure two phones and then test the connectivity, call between phones and voicemail to test
- configure the balance of the extensions
- When configuring a trunk, set it up and then test prior to full implementation.
- On SIP trunks, configure the trunk and then test inbound and outbound.
- On a PRI to check DID and make sure it is delivered correctly and only then program the balance of the DID’s.
When installing remote phones this method is also advantageous. To verify prior to rollout of all remote phones a single phone should be installed and tested to verify that the port configuration is all accurate.
Once all elements are configured and test correctly then you should proceed with the remainder of the install.