Training: vLAN
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Virtual LANs (vLANs)
Overview
Virtual LANs (vLANs) are a pivotal concept in modern networking, providing a logical method to segregate network traffic for reasons primarily related to security and efficiency. Unlike traditional LANs, vLANs do this without the need for separate physical networks.
Switch Port Types in vLANs
Access Ports
- Function: Designed for single vLAN membership.
- Usage: Ideal for devices like PCs or phones that don't support vLAN tagging.
- Limitation: Each port can only belong to one vLAN, limiting the use of multiple devices requiring different vLANs on the same port.
Trunk Ports
- Function: Capable of carrying multiple vLANs simultaneously.
- Configuration: Can be set to carry specific vLANs, distinguishing them using tags.
- Default Behavior: Untagged traffic is assigned to a default vLAN.
vLAN Traffic Types
Untagged Traffic
- Definition: Standard network traffic without vLAN identification.
- Assignment: Automatically assigned to the port's default vLAN.
Tagged Traffic
- Definition: Contains a vLAN ID (VID) to direct it to the appropriate vLAN.
- Security: Ports not configured for a specific VID will reject its traffic, enhancing network segmentation.
Setting Up vLANs
Deciding on DHCP Server
- Options: Choose between the router or the PBX system to manage DHCP for the vLAN.
- Considerations: This decision influences subsequent network configurations.
Configurations
Router as DHCP Server
- PBX Settings: Disable VLAN on the PBX system. Configure it to send untagged voice traffic.
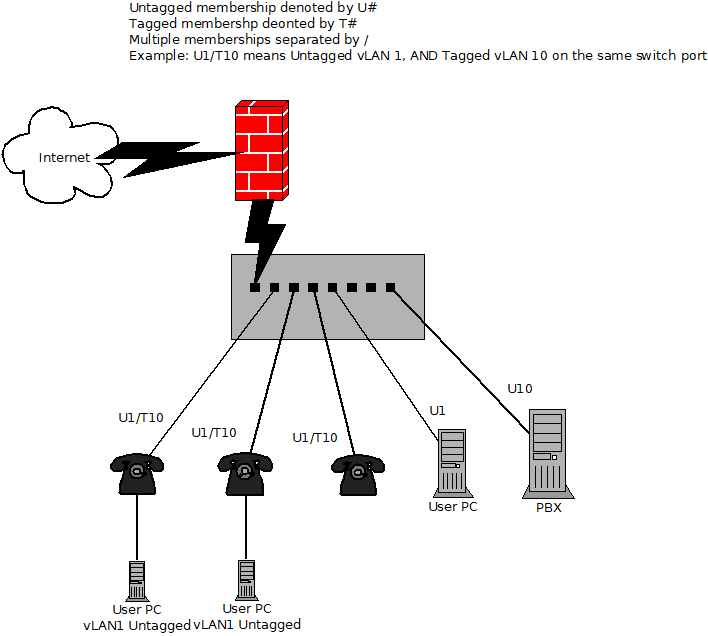
- Switch Port Configuration: Set the PBX-connected port as an untagged member of the voice vLAN.
PBX as DHCP Server
- PBX Settings: Enable VLAN with a unique IP address and subnet mask. Set the maximum DHCP leases.
- Switch Port Configuration: Configure the PBX-connected port as a tagged member of the voice vLAN and untagged in the data vLAN.
Switch Configuration for Phones
- Requirement: Ports for phones should be members of both data (untagged) and voice (tagged) vLANs.
- Purpose: Ensures proper segregation of phone traffic and PC access to the data network.
Inter-vLAN Communication Rules
- Rule: Ports in a specific vLAN (e.g., vLAN 10) can only interact with ports in the same vLAN.
- Exception: Ports in different vLANs can communicate only if configured as members of the relevant vLANs.
PBX Configuration for Voice vLAN
System Settings for vLAN
- Enable vLAN: Set to 'Enabled' to activate vLAN functionality on the PBX system.
- vLAN IP Address: Assign an IP address that the phones will use to reach the PBX. Defaulting to 10.71.66.1 is usually adequate. Ensure this is distinct from the PBX's primary network interface to avoid conflicts.
- vLAN Subnet Mask: Use 255.255.255.0 for up to 254 usable addresses, sufficient for most phone networks.
- vLAN ID (VID): Default is 10. Adjust to match the voice vLAN ID configured on your switches.
- Max DHCP Leases: Set to cover the anticipated number of phones but within the limits of your subnet (total addresses in the subnet minus one for the PBX).
PBX Global Phone Settings
- Apply vLAN Config to Phones: Set to 'Enabled' to apply vLAN settings to connected phones.
- Phone vLAN Enable: Enable this to tag voice traffic from phones.
- Phone VID: Match this with your voice vLAN ID.
- Phone Priority: Not used in current configurations.
- PC vLAN Enable: Typically disabled unless tagging PC traffic through the phone's passthrough port.
- PC VID: Set if using a data vLAN for PCs connected through phones. Requires PC vLAN to be enabled.
- PC Priority: Currently not utilized.
Switch Configuration for PBX and Phones
- PBX Port Setup: Configure the switch port connected to the PBX as:
- Untagged in the data vLAN (for communication with SIP trunks and other network services).
- Tagged in the voice vLAN (for communication with phones).
- Phone Ports Setup: Ports connecting to phones should be:
- Untagged in the data vLAN.
- Tagged in the voice vLAN, as phones will send/receive tagged voice traffic.
- PCs connected to phone passthrough ports will send their data traffic untagged.